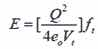http://www.i-sis.org.uk/The_Z_theory_of_everything.php
The velocity of 1.094 million metres per second is the result of a classical impedance match – a match that allows energy to flow directly without resistance within the atomic structure - when the velocity of light in the outer electronic orbitals of the atom equals the velocity of sound within its nucleus, i.e., 1.094 million metres per second, and energy transfer can take place with 100 percent efficiency. The 100 efficient process emits one photon, not a series of progressively smaller photons that would be emitted by less efficient non-impedance matched system.
Fmax of 29.05 Newtons at the radius of the electron re(which is half the classical radius of the electron). The elastic constant, K-e, which determines the magnitude of the restoring force, is an inverse function of the displacement rx multiplied by Fmax.
K-e = Fmax / rx
The frequency of this harmonic motion fn, is given by Equation (2B) (the division by 2pconverts angular frequency to frequency in Hertz, and Mn is the mass of the nucleon).
fn = 1/2p √( K-e /Mn)
The velocity Vt emerges as the product of the frequency at a displacement equal to twice the momentum spacing of the nucleons, rn of 1.36 x10-15 m (larger than the radius of a proton because of movement of adjacent nucleons)
The fine structure constant in its current value is 7.2973525698 x 10-3 or approximately 1/137 [30]. It is defined in terms of other fundamental constants, and the simplest formula is Equation (5), where e is the elementary charge, ћ = h/2p is the reduced Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light in vacuum, and ke is the Coulomb constant. Its origin remains obscure, however.
a = kee2/ћc
a = 2Vt/c
Vt, the velocity of quantum transition, is that at which the velocity of light within the electronic structure of the atoms equals the velocity of sound within its nuclear structure and the impedance of the interacting states are matched, so energy is exchanged “without bounce” (i.e. with no barrier and at 100 percent efficiency). That is what accounts for the quantization of energy levels in the atom. Electrons attempt to flow along all possible paths but they can only move between orbits through channels of matching impedance. Znidarsic shows that Planck’s constant is based on Vt , which also determines the energy levels of the Bohr hydrogen atom and the intensity and probability of its spectral emissions. The energy of the photon is given by Equation (2) where Q is the elementary charge, and eo is the electric permittivity of free space.
[These equations derive quantum mechanics from classical Newtonian mechanics. It treats light like a capacitor and electrons like springs. (spring theory?)]